Arithmatical – Alligation or Mixture
DIRECTIONS : Important Facts and Formulae
| 11. |
In what ratio must a grocer mix two varieties of pulses costing Rs.15 and Rs.20 per kg respectively so as to get a mixture worth Rs.16.50 per Kg? |
| |
A. 3 : 7 |
| |
B. 5 : 7 |
| |
C. 7 : 3 |
| |
D. 7 : 5 |
| Solution |
| |
|
By the rule of alligation: |
| Cost of 1 kg pulses of 1st kind |
Cost of 1 kg pulses of 2nd kind |
 |
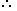 Required ratio = 3.50 : 1.50 = 35 : 15 = 7 : 3. Required ratio = 3.50 : 1.50 = 35 : 15 = 7 : 3. |
|
| 12. |
8 litres are drawn from a cask full of wine and is then filled with water. This operation is performed three more times. The ratio of the quantity of wine now left in cask to that of the water is 16 : 65. How much wine the cask hold originally ? |
| |
A. 18 litres |
| |
B. 24 litres |
| |
C. 32 litres |
| |
D. 42 litres |
| Solution |
| Let the quantity of the wine in the cask originally be x litres |
then, quantity of wine left in cask after 4 operations
= [x(1- 8/x)4] litres. |
Therefore x(1- 8/x)4 / x = 16/81 =› (1- 8/x)4 = (2/3)2
=› (x - 8 / x) = 2/3 =› 3x - 24 = 2x =› x = 24.
|
|
| 13. |
A jar full of whiskey contains 40% alcohol. A part of this whisky is replaced by another containing 19% alcohols and now the percentage of alcohol was found to be 26%. The quantity of whisky replaced of whisky replaced is |
| |
A. 1 / 3 |
| |
B. 2 / 3 |
| |
C. 2 / 5 |
| |
D. 3 / 5 |
| Solution |
| |
|
By the rule of alligation: |
| Strength of first jar |
Strength of second jar |
 |
| So, ratio of 1st and 2nd quantities = 7 : 14 = 1 : 2. |
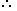 Required quantity replaced = 2/3 Required quantity replaced = 2/3 |
|
| 14. |
A merchant has 1000 kg of sugar part of which he sells at 8% profit and the rest at 18% profit. He gains 14% on the whole. The Quantity sold at 18% profit is |
| |
A. 400 kg |
| |
B. 560 kg |
| |
C. 600 kg |
| |
D. 640 kg |
| Solution |
| |
|
By the rule of alligation: |
| Profit of first part |
Profit of second part |
 |
| So, ratio of 1st and 2nd parts = 4 : 6 = 2 : 3. |
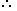 Quantity of 2nd kind = (3/5 x 1000)kg = 600 kg. Quantity of 2nd kind = (3/5 x 1000)kg = 600 kg. |
|

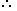 Required ratio = 3.50 : 1.50 = 35 : 15 = 7 : 3.
Required ratio = 3.50 : 1.50 = 35 : 15 = 7 : 3.
